ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is the English abbreviation for Enterprise Resource Planning. Generally, ERP includes distribution, manufacturing, and finance in enterprise applications. Therefore, the ERP system is a continuation of MRP (Manufacturing Resource Planning). More accurately, ERP is based on MRPII. At present, more are conceptual products, such as financial software plus importing, selling, and depositing to become ERP. In theory, ERP may involve modules: forecasting, order management, sales analysis, purchase management, warehouse management, inventory control, production planning (MPS), product data management (PDM), material requirement planning, capacity requirement planning (CRP) ), distribution demand planning (DRP), shop floor control (SFC), process operation management, quality management, salary management, human resources, etc. nearly 30 modules. ERP is essentially different from OA, and ERP tends to be business management.
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is the production process execution system of the manufacturing enterprise, and it is a set of production information management systems for the execution layer of the manufacturing enterprise workshop. MES can provide companies with manufacturing data management, planning and scheduling management, production scheduling management, inventory management, quality management, human resource management, work center/equipment management, tooling management, procurement management, cost management, project kanban management, production Process control, bottom-level data integration analysis, upper-level data integration and decomposition, and other management modules, create a solid, reliable, comprehensive, and feasible manufacturing collaborative management platform for the enterprise.
The MES system is mainly used to solve the problem of disconnection between the production plan and the production process in the overall optimization of smart factory planning. This problem has directly affected enterprises' production efficiency for a long time and has become a bottleneck restricting manufacturing enterprises from achieving intelligent manufacturing upgrades, integrating internal information of enterprises, and optimizing supply chains between enterprises.
Enterprise ERP system and MES system are an important combination for enterprises to achieve overall management planning. The former lies in the overall management and control of the entire enterprise and the group enterprise, and the latter focuses on the management of the workshop site. The two seem to be quite the same, but in reality, there are still differences in management.
Specifically, there are the following aspects:
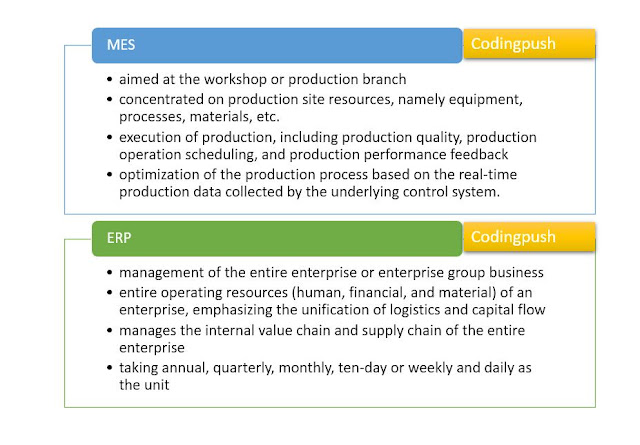
ERP is the management of the entire enterprise or enterprise group business, while the management of MES is aimed at the workshop or production branch. Even the most complete MES system, for the entire enterprise, only provides a relatively narrow perspective, lacking the breadth and depth of data required for management and decision-making.
ERP is the management of the entire operating resources (human, financial, and material) of an enterprise, emphasizing the unification of logistics and capital flow, which is the so-called "integration of business and finance." The management of MES is more concentrated on production site resources, namely equipment, processes, materials, etc.
ERP manages the internal value chain and supply chain of the entire enterprise, that is, sales, procurement, production, inventory, quality, finance, human resources, etc., emphasizing the integration of all these businesses, and emphasizing the planning (sales plan, production plan, purchase plan, etc.) Coordination and control; MES mainly manages the execution of production, including production quality, production operation scheduling, and production performance feedback.
ERP has a relatively wide period of time for planning and business management, taking annual, quarterly, monthly, ten-day or weekly, and daily as the unit; due to the need for production site management and control, the management of MES is more detailed and manages to days, shifts, and hours. Under the guidance of the long-term plan generated by the ERP system, MES conducts short-term production planning and scheduling, monitoring, resource allocation, and optimization of the production process based on the real-time production data collected by the underlying control system.
Summary: The above four points show that MES and the company's ERP system are different and highly related. As long as the two are highly integrated and each performs its own duties, it can bring the company's best work efficiency and economic benefits.
Comments
Post a Comment